Function of tuft cells in heath and disease





Their unique morphology led to the identification of tuft cells (also called brush cells) more than half a century ago. Because of the lack of appropriate markers, they have since remained overlooked in functional studies of the intestinal epithelium.
We have recently characterised mouse and human intestinal epithelial tuft cells. These rare cells express the DCLK1 marker, previously considered as a putative quiescent stem cell marker in the intestinal epithelium (Gerbe et al., Gastroenterology 2009, vol. 137: 2179). We demonstrated that DCLK1+ cells are instead post-mitotic tuft cells, which are short lived and permanently renewed from Lgr5+ stem cells. According to their unique genetic requirements to differentiate, we proposed that tuft cells constitute a fifth differentiated cell type in the intestinal epithelium (Gerbe et al., J. Cell Biol. 2011, vol. 192: 767-780. See also an Editorial comment here).

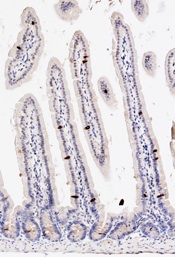
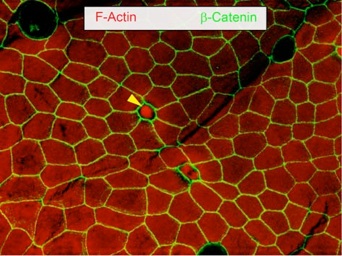
Tuft cells in the intestinal epithelium. Left panel: revealed by Dclk1 expression (DAB). Right panel revealed by higher F-Actin immunoreactivity (red).